Angles are a fundamental notion in geometry, essential for comprehending shapes, motion, and space. They may be seen everywhere, from building architecture to computer screen layouts. They are measured in degrees (°) or radians and are crucial in various mathematical and real-world applications, from architecture to astronomy.
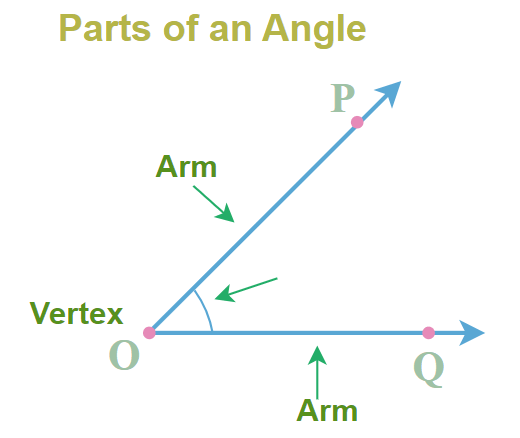
An angle is formed when two rays (or line segments) share a common endpoint. This common endpoint is called the angle's vertex, and the two rays are referred to as the sides or arms of the angle. The amount of turn between the two rays around the vertex measures the angle.
Understanding the parts of an angle is essential for identifying and working with angles in various mathematical and practical contexts. The main parts of an angle include:
Angles can be classified into various types based on their measurements and relationships. Here are the most common types of angles:
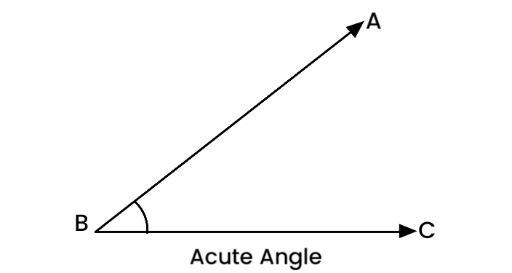
An acute angle measures greater than 0° and less than 90°. These angles are small and sharp. For example, a 30° angle is an acute angle.
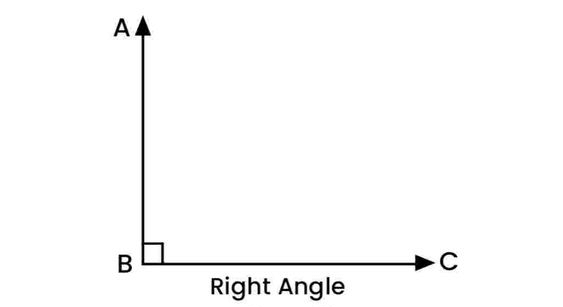
A right angle measures exactly 90°. A small square at the vertex often represents it. Right angles are commonly found in squares and rectangles.
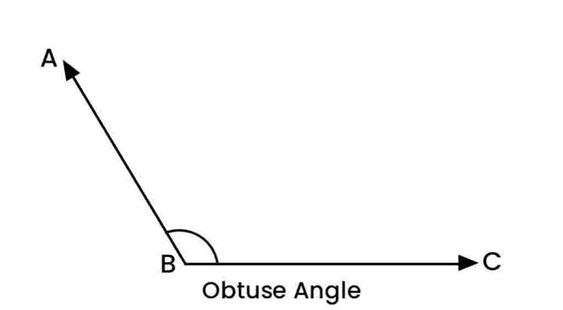
An obtuse angle measures greater than 90° but less than 180°. These angles are larger and more open than acute angles. For example, a 120° angle is an obtuse angle.
A straight angle measures exactly 180°. It forms a straight line, hence the name. Straight angles are essentially two right angles combined.
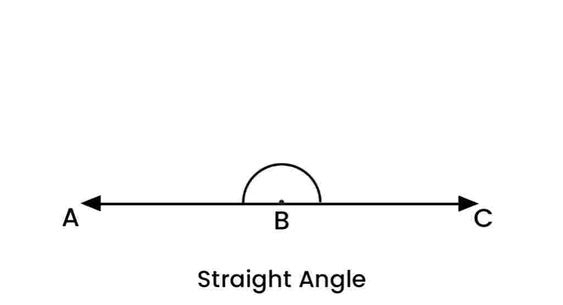
A reflex angle measures greater than 180° but less than 360°. These angles are more than half a circle but less than a full circle. For example, a 270° angle is a reflex angle.
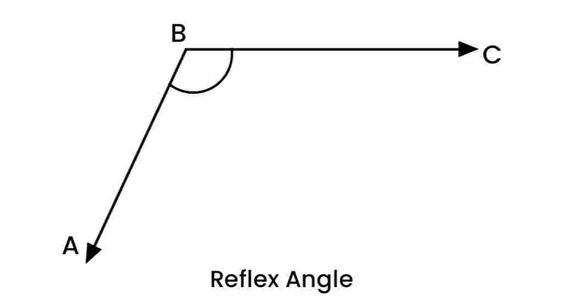
A full rotation angle measures exactly 360°. It represents a complete rotation around a point.
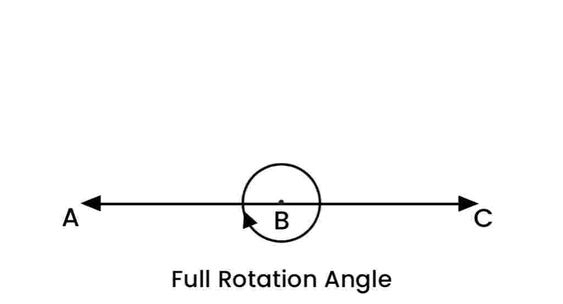
Adjacent angles share a common vertex and a common arm but do not overlap. They lie next to each other.
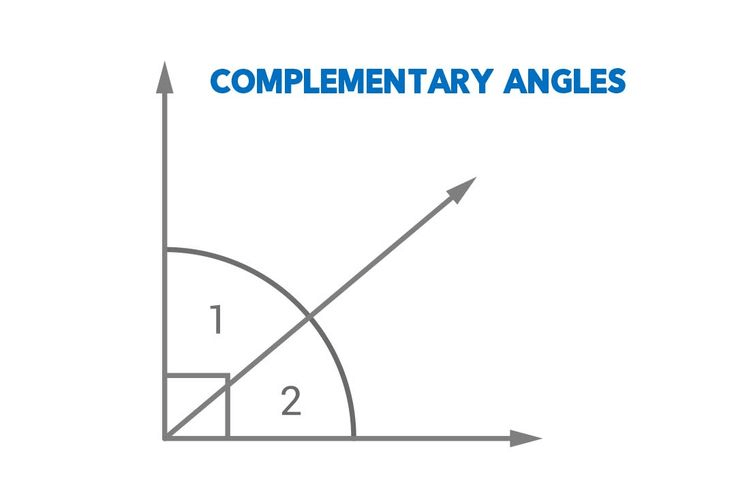
Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90°. For instance, if one angle measures 30°, the other must measure 60° to be complementary.
Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is 180°. For example, if one angle measures 110°, the other must measure 70° to be supplementary.
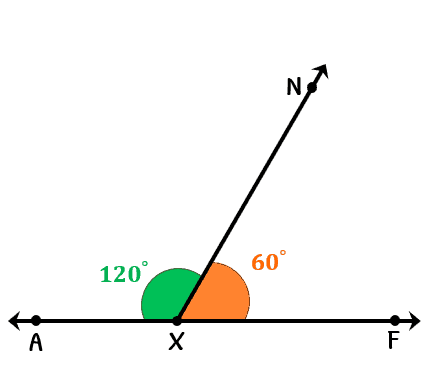
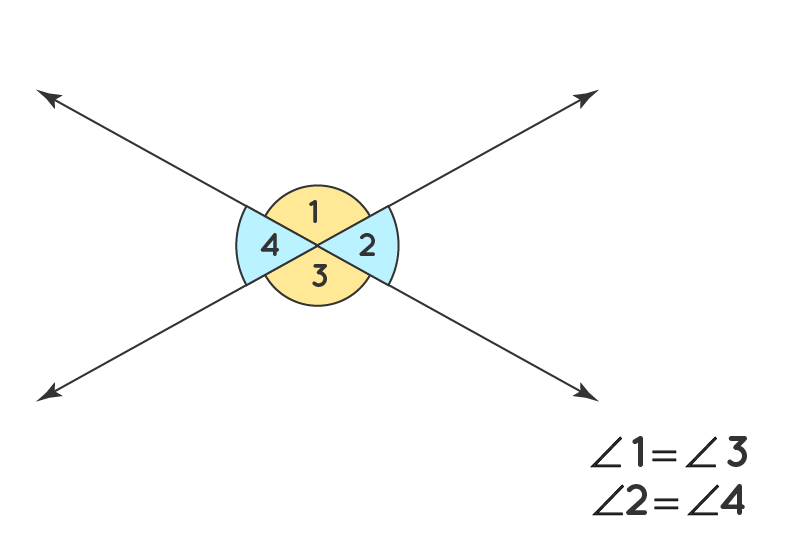
Vertical angles are formed when two lines intersect. They are opposite each other and are always equal in measure.
Angles are typically measured using a protractor, which can measure angles in degrees. There are also mathematical methods for calculating angles using trigonometric functions. Understanding how to measure angles is crucial for solving geometry problems and various applications in science and engineering.
Angles can also form special pairs, which include:
Examples of Angles in Real Life
Understanding angles is fundamental to mastering geometry. From their basic definition and parts to the various types and real-world examples, angles are a crucial element in both mathematics and everyday life. By grasping these concepts, students can better appreciate angles' practical applications and importance.
In geometric terms, angles are typically measured up to 360°. However, in certain contexts, angles can exceed 360°, representing multiple rotations.
Complementary angles add up to 90°, while supplementary angles add up to 180°.
Angles are measured in degrees (°) or radians.
An angle is formed by two rays with a common endpoint called the vertex, and it measures the amount of turn between the two rays.
What Makes the IB Diploma an Excellent Choice? Explore 10 Compelling Reasons to Pursue IBDP in High School.
© Knowledgeum Academy

